User guide
Quick Start Guide
Dashboard
Overviews
Case detail (Caseoverview)
Case - event
Tasks
Case notes
Documents
User settings
Favorites
Table component
FAQ
News/Announcements in Team assistant
Mobile app settings
Administrator Guide
Platform guide
Administration
Crons
Authentication and Synchronization
Mobile App Setup for Your Environment
Scheme
Dynamic tables
Archiving
Scripts
Service console
Scheduled Tasks
HR Agenda
Sequences
CSP Headers
Logs
Access Token Settings & Session Expiration
Template
Roles
Planning
Users
Organizational structure
Events
Translations
AXIOS API
Calculations & Functions
Integrations
TAS Forms
TAS Forms
Activating the module on the environment
TAS Forms - secret creation guide for Docker Swarm
Advanced Features & Tips
Partners
Product
Technical Changelog
Business Changelog
Version Upgrade Guide
Upgrading to 5.9
Upgrading to 5.3
Dynamic conditions migration
PDF printing adjustment
Editing Task Description vs Task Instructions
Transpiling forEach to a for loop
Rendering HTML on Caseoverview
Upgrading to 5.7
Lodash upgrade v4.17.x (>v5.5)
Main changes and deprecated features (v5.3 > v5.7)
Highlighting variables in Read-only status (>v5.7.58)
Using validation functions
Differences between TAS4 and TAS5 - a complete overview
Best Practices for Upgrading from v4 to v5
Technical details
News / Important information
- All Categories /
- Administrator Guide
- Platform guide
- Administration /
- CSP Headers
CSP Headers
Content Security Policy (CSP) is a security mechanism that helps protect web applications from attacks such as Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) and other code injection threats. CSP allows administrators to define which resources—such as scripts, styles, and images—can be loaded and executed on a page. By enforcing CSP, the platform reduces the risk of malicious code compromising the application.
Configuration Location
CSP settings can be configured in the platform under the Configuration section, specifically in the Security tab. This section contains all available security headers.
Path:
.../administration/configuration/security
Setting CSP Headers
Detailed explanations and examples of configuring individual CSP headers can be found in the Helmet npm package documentation.
To configure CSP in the platform, insert the contentSecurityPolicy object into the configuration as JSON. Ensure the JSON structure is valid by adding double quotes around keys and values and removing any extra commas.
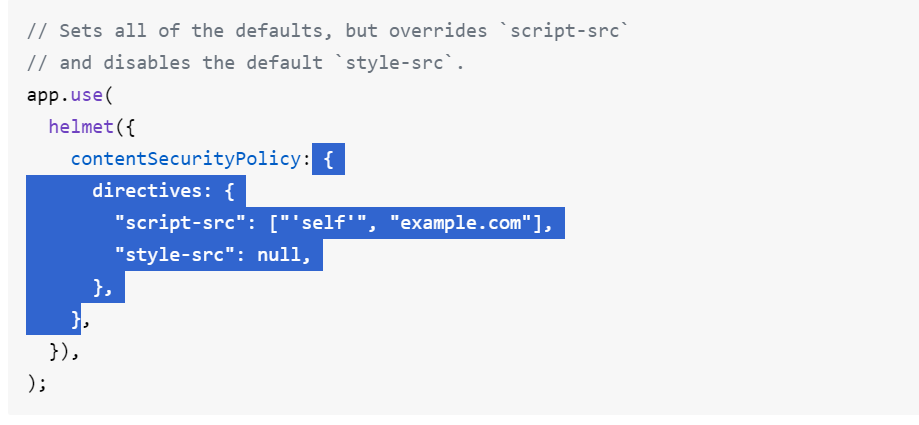
Example Configuration
Basic CSP Configuration
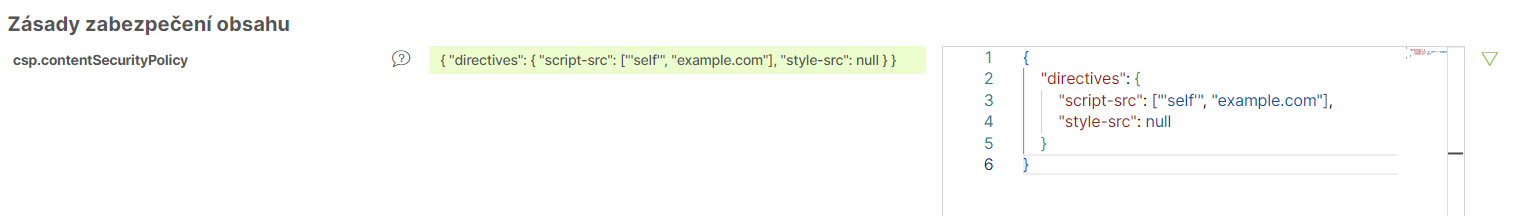
{
"directives": {
"script-src": ["'self'", "example.com"],
"style-src": null
}
}Default CSP Configuration in Team assistant
//csp.contentSecurityPolicy
{
"directives": {
"default-src": ["'self'"],
"script-src": ["'self'"],
"style-src": ["'self'"],
"img-src": ["'self'"],
"font-src": ["'self'"],
"connect-src": ["'self'"],
"frame-ancestors": ["'self'"],
"base-uri": ["'self'"],
"form-action": ["'self'"],
"object-src": ["'none'"],
"media-src": ["'self'"],
"worker-src": ["'self'"],
"child-src": ["'self'"],
"manifest-src": ["'self'"]
}
}
//csp.crossOriginEmbedderPolicy
{"Cross-Origin-Embedder-Policy": "require-corp"}
//csp.crossOriginOpenerPolicy
{ "Cross-Origin-Opener-Policy": "same-origin"}
// csp.crossOriginResourcePolicy
{"Cross-Origin-Resource-Policy": "same-origin"}
//csp.originAgentCluster
true
//csp.referrerPolicy
{ "Referrer-Policy": "no-referrer-when-downgrade"}
//csp.strictTransportSecurity
{ "Strict-Transport-Security": {
"max-age": 31536000,
"includeSubDomains": true,
"preload": true
}}
//csp.xContentTypeOptions
true
//csp.xDnsPrefetchControl
{"X-DNS-Prefetch-Control": "off"}
//csp.xDownloadOptions
true
//csp.xFrameOptions
{ "X-Frame-Options": "DENY"}
//csp.xPermittedCrossDomainPolicies
{"X-Permitted-Cross-Domain-Policies": "none"}
//csp.xPoweredBy
true
//csp.xXssProtection
true
Best Practices
- Test in a Development Environment – Before applying CSP policies in production, test them in a development or staging environment to avoid locking users out.
- Use a CSP Report-Only Mode First – Before enforcing strict policies, use CSP's report-only mode to gather potential issues without blocking content.
- Gradually Increase Restrictions – Start with a basic policy and gradually tighten restrictions as you identify necessary exceptions.
- Regularly Review CSP Reports – Monitor reports for blocked resources and adjust policies accordingly.
By correctly configuring CSP in the platform, administrators can significantly enhance security and minimize risks associated with malicious code execution.
Updated
by Anna Gernát
